Refugees need better mental health support amid rising displacement
Refugees need better mental health support amid rising displacement
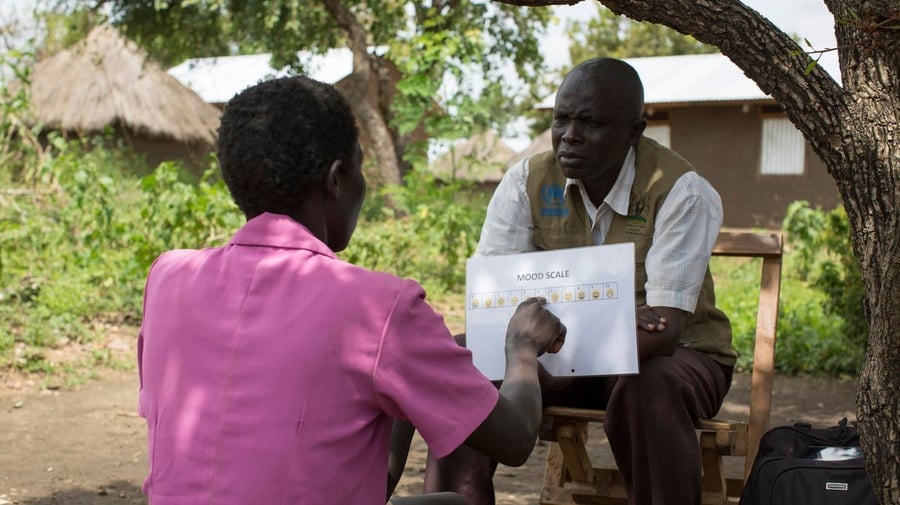
A South Sudanese refugee assesses her mood on a pictorial scale during a psycho-social counselling session in Uganda's Bidibidi settlement.
GENEVA – Refugees demonstrate great resilience in the face of life-altering circumstances but need increased support for mental health services, UNHCR, the UN Refugee Agency, said.
According to new figures out this week, UNHCR provided mental health and psychosocial support services to over 472,000 refugees, asylum-seekers and their families and caregivers in the first half of 2022.
Although strides are being made to improve access to psychosocial support, UNHCR is concerned that the worsening socio-economic outlook and rising food insecurity in many refugee hosting countries could compound existing pressures on refugees.
“The best way to improve the mental health of refugees is to find lasting solutions to the crises they are fleeing,” said Sajjad Malik, Director for the Division of Resilience and Solutions. “We know that the experience of displacement takes a huge toll on emotional and social well-being and it is the right of every refugee to be able to access appropriate care and support.”
Refugees are exposed to stress at every stage of their displacement. Pressures include separation from families, xenophobia, lack of livelihood opportunities, perilous journeys and exposure to conflict and persecution. A recent survey conducted by UNHCR and the World Bank in Uganda found rates of depression among refugees were markedly higher than among people living in host communities.
Today, UNHCR’s Executive Committee adopted a conclusion acknowledging the mental fortitude of forcibly displaced people, urging increased availability of mental health and psychosocial support services to refugees and other displaced and stateless people, including access to national health and social services.
In 2021, 1,683 primary healthcare staff in refugee settings were trained to identify and manage mental health issues across 19 countries.
Speaking about the conclusion, which came days after marking World Mental Health Day on Monday, Malik said he was encouraged by the commitment of states to prioritize mental health and psychosocial support in the international response to displacement.
Part of ensuring that refugees are well cared for, is to make sure that humanitarian staff are also in good mental health, he added. “The priority is to improve mental health support for refugees, but we must also ensure that humanitarians are in the best possible condition to serve the people who need us most,” Malik said.
The Executive Committee conclusion also highlights the need to include mental health and psychosocial support when planning for refugee responses and encourages states to integrate refugees and displaced people into national services and existing care systems. Its adoption represents a significant acknowledgement by states in different regions and circumstances of the importance of mental health and psychosocial support for displaced and stateless people worldwide.
The UNHCR Executive Committee is a subsidiary body of the UN General Assembly, comprising 107 member states, that advises the High Commissioner on international protection and approves the programme budget.
For more information on this topic, please contact:
- In Geneva, Yuko Narushima, [email protected], +41 79 863 7327
- In New York, Kat Mahoney, [email protected], +1 347 574 6552









